Design and construction of barns
Typical frame barn for 200 heads
Typical barn designs
Most often, large modern livestock farms and complexes are located in buildings that have survived from Soviet times. Converting an old building is much cheaper than building new space. This is especially true when it comes to large livestock and a barn for 100 heads or more. Old buildings are distinguished by their reliability and convenient layout: very often the buildings are interconnected, have a special room for organizing a dairy shop, a maternity barn, a separate barn for calves, young bulls and heifers, and breeding stock. With the same success, you can convert an old stable or pigsty or sheepfold into a cowshed.
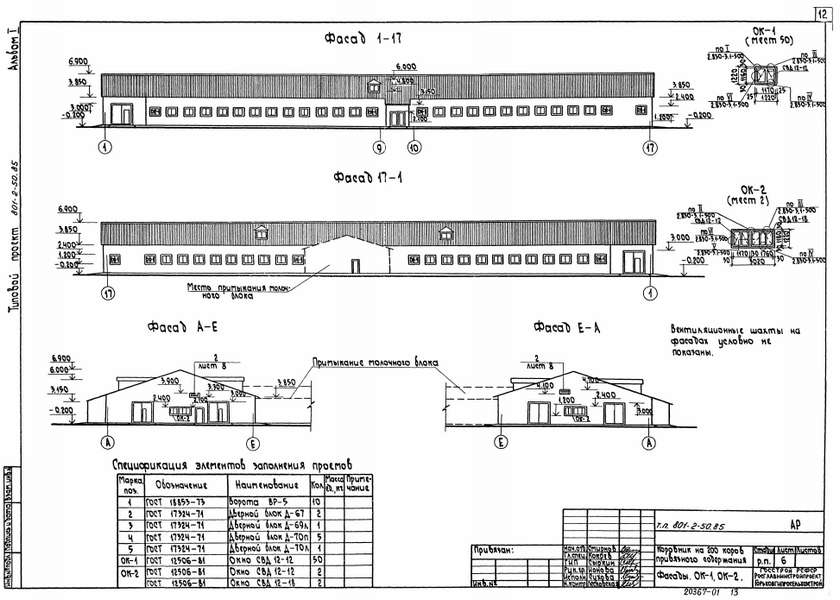
Barn project for 200 heads
In modern livestock farming, farms are most often built from scratch for livestock from 50 to 200 cows.
For larger livestock, it is more profitable to find and refurbish a ready-made barn. At the first stage of planning and creating a project, it is necessary to decide on the number of cows and the maintenance system. This can be stabling, in common pens or on a leash.
It is most convenient to use a standard barn design - a one-story building with a wall height of about 3 meters, an insulated roof, and a maximum height under the ridge of 3.5 meters. At this height, good natural air circulation will be ensured. For construction, it is better to use a material that is suitable for the given climatic conditions, economical and environmentally friendly. Most often used:
- Metal,
- Sandwich panels,
- Foam concrete,
- Brick,
- Beam.
Features of barn ventilation
Natural ventilation in a typical barn is provided by the presence of small windows under the roof ridge. And forced ventilation of the barn requires a special device - a tunnel or circulation fan. Such fans are most often installed under the ridge of the roof, and can operate either automatically or be turned on as needed.

Summer barn, tent hangar
Typical dairy farm project
Typical dairy farm projects designed for large livestock (from 400 to 2800 or more heads) have their differences. The construction of such a livestock complex should include eight sections. Each section will be occupied by cows selected according to physiological and biological parameters (age, milk production, lactation period, etc.).
The design of a complex for keeping cattle with a livestock of 2000 animals often includes premises for organizing a dairy plant. For a large farm, this is more profitable than selling milk in large volumes to third parties.
Modern barns designed for large numbers of cattle must be at least 102 meters long (for 460 animals) and at least 120 meters long (for 1100 animals). Typically, a typical dairy farm project involves keeping cows freely without a leash, in boxes, on a bed of straw or sawdust.
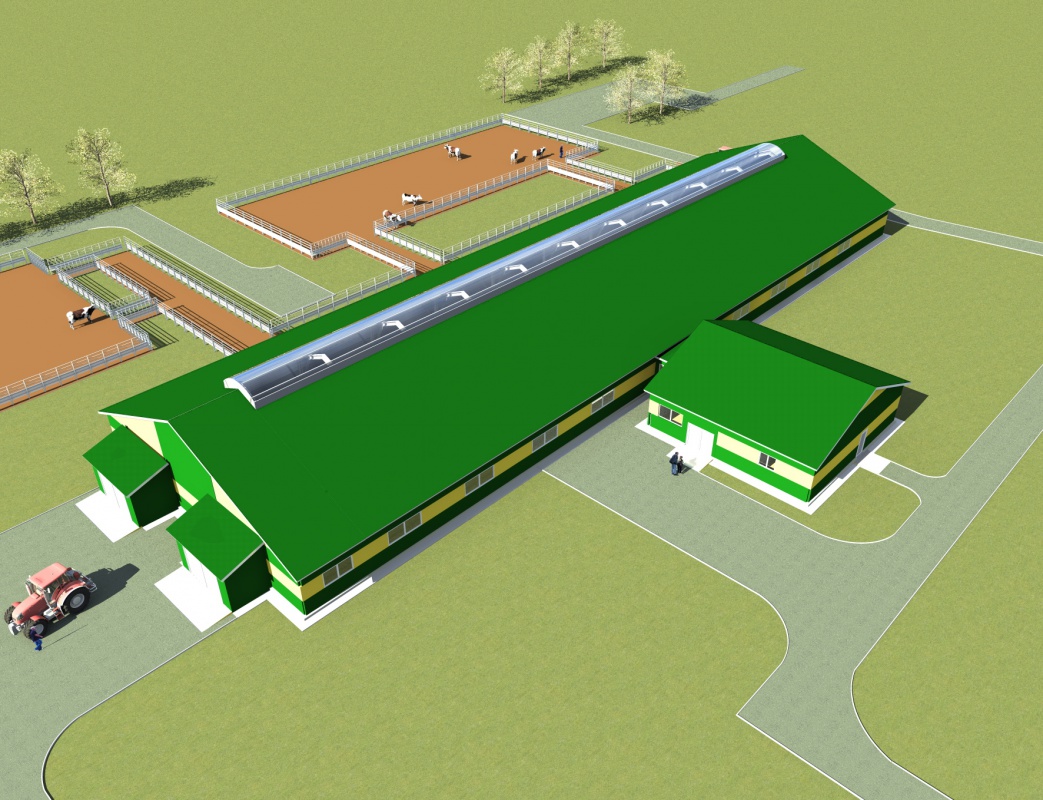

Barn project general view
A large dairy farm also involves the organization of a milking parlor equipped with automatic milking equipment. It will take two employees about four hours to service a herd of 400-600 head, while larger herds typically require three to five milking parlor workers.
In addition to the milking and birthing parlor, a typical dairy farm design includes:
- Veterinary inspection and quarantine area,
- Transport hall,
- Feed storage warehouse,
- Office premises for employees,
- Veal barn,
- Vehicle scales and disinfection system,
- Garage,
- manure pit,
- Fire tank.
All large commercial dairy farms are equipped with special devices that distribute water and feed automatically.
For a farm of 600 heads, the minimum required area is about 1,200 hectares of land. And the annual productivity of such a complex will be about 8,000 tons of milk and 200 tons of meat. The construction estimate from scratch will be more than 350 million rubles.
Features of the barn design for 100 and 200 heads
The design of a barn for 100 heads most often involves keeping cows tied in stalls, since this is a more economical option. Stall size for one animal: length - 2 meters, width - 1.2 meters. The floor in the barn is designed taking into account a slight slope - no more than 2.5 cm. This makes cleaning the entire room easier. A typical barn plan includes utility rooms, a cesspool, a water system, heating, electricity, as well as marking out the installation of the necessary milking equipment.
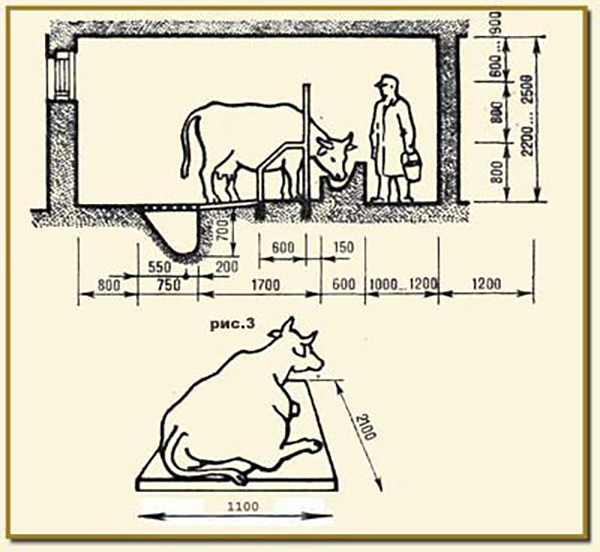
Calculation module for design
The design of a barn for 200 heads is different in that it involves the arrangement of stalls in four rows. A 200 head barn is the same as a 100 head barn with an area of less than 1500 sq.m. does not require passing state examination.
Features of the barn design for 50 heads or less
For a homestead, where there are from one to five cows, a cattle shed is much more common. Cows are often kept together with goats, poultry, piglets and other domestic animals. If there are more cows, then farmers build a private dairy farm using a barn design for 20 heads or more.
According to one standard project, you can build a barn for 5 heads or a barn for 50 heads: there is no significant difference in construction.
You can build such a farm yourself, without the help of construction companies. You just need to decide on a sufficient plot of land, develop a farm plan that would take into account the supply of all communications, an air exchange device, separate stalls for breeding bulls and dairy cows, as well as a cesspool.
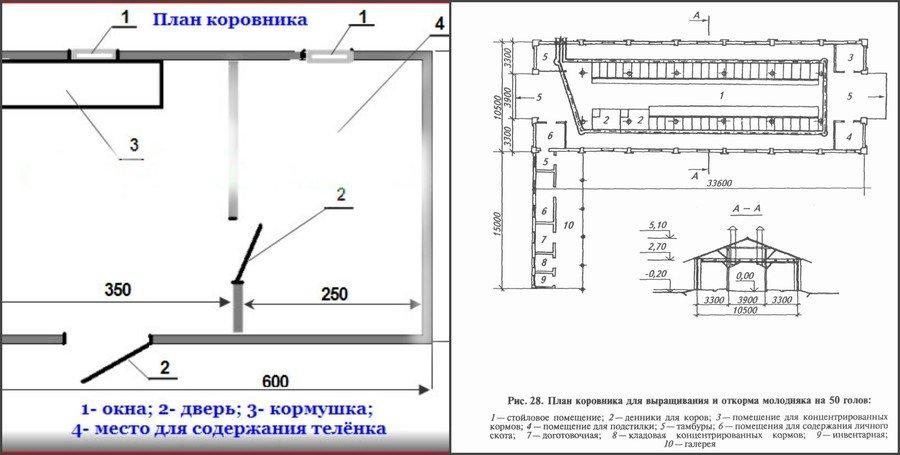
Barn for 1 cow and calf
A detailed diagram of the farm should also include a room for storing equipment, marking stalls and aisles with all dimensions, the location of switches and sockets, and water taps.
Barn Construction Methods
Before you build a barn with your own hands, you need to prepare the site for construction. A layer of fertile soil is removed from the site, after which the site is covered with medium-sized crushed stone. This site preparation allows for sufficient foundation hardness. When building a barn yourself, two methods are used: frame and frameless.
Frame method
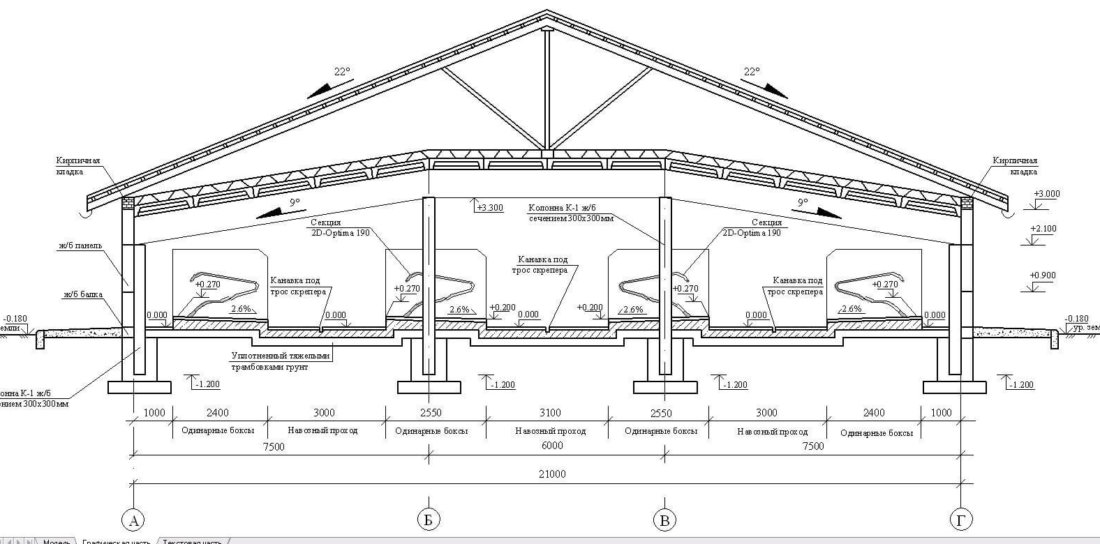
Building a barn using this method is more economical. Immediately after preparing the soil, installation of the frame begins. First, the support of the future structure is laid in the base in the shape of a square, then they begin to install the support pillars. All supporting elements are connected to each other using a welding machine.
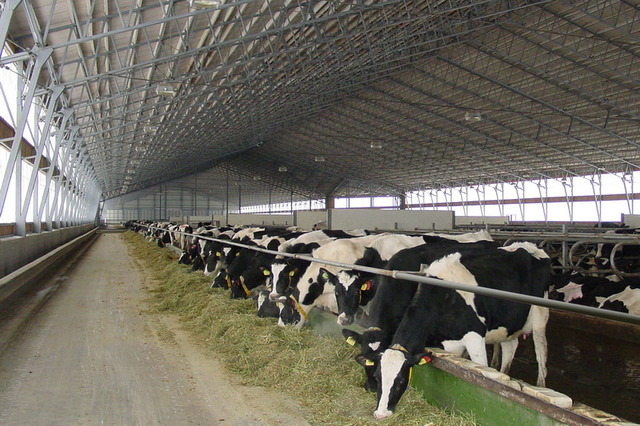

Typical frame barn for 200 heads
Frameless method
The second method is frameless, which involves the mandatory construction of a foundation. There are two ways to build a foundation correctly. First: we build the formwork and fill it with concrete. Second: we fill the dug trench with rubble stone and burnt brick, and connect them with cement. If the soil is not loose, then the depth of the foundation is about 60 cm. The walls are erected directly on the foundation, without using any support pillars.
General principles of construction
In farms engaged in breeding and keeping cattle, the minimum height of the walls should be about 2.5 meters, and the ceiling height along the central aisle should be at least 3.5 meters. When designing walls, you should definitely consider the presence of windows. To reduce electricity costs, it is recommended to make the number of windows equal to the number of animals. So, in the walls of a barn for 20 heads there should be at least twenty windows. After the walls are erected and the roof is covered, they begin concreting the floor and constructing internal partitions.
Organization of the delivery room
When thinking through the drawings for the construction of a barn, it is necessary to mark out not only the main room, but also the maternity unit, the feeding area, the walking area and the milking parlor.
The birth hall is located in the warmest part and is equipped with double doors. This will help avoid drafts. In the birth stall, they make larger stalls (for a cow with a calf, at least 10 sq.m. is required), additional lighting is provided, and automatic drinking bowls are installed. The stall is covered with double bedding. It is very important to provide water supply with convenient taps in the delivery room. All partitions are made only from wood.
Organization of feed
Each stall must be equipped with a feeder and a manger for hay, as well as a drinking bowl or automatic drinking bowl. But it is also important to organize a place to store feed. Hay and straw are most often stored under a shed next to the barn, but concentrated feed and grain should be stored indoors. Typically, barns have a separate room for feed. Several shelves are made in it, a bath is installed (for steaming food and preparing mash), as well as several containers with a convenient lid system for storing grain. In the stern you can also put a small refrigerator for storing oils, medicines, and liquid fertilizers.
Organization of a milking parlor
Even on a small farm it is better to provide a room for arranging a milking parlor. For a livestock of 10 - 20 cows, it is enough to equip two stalls, next to which milking equipment should be placed, with convenient access to electricity and water. The stalls must be equipped with mangers for hay. Stalls are made from both metal pipes and timber. The most convenient option for a milking device for a small herd is a pair milking machine.
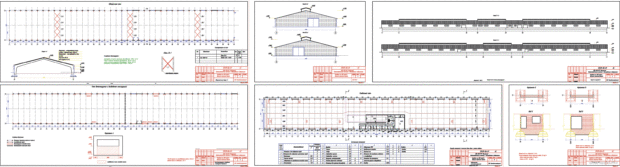
Set of documentation for a barn
The milking parlor should have both good lighting and good ventilation.
On large farms, a separate room is allocated for the milking parlor, where complex milking equipment and a milk pipeline system are located. The layout of the milking parlor and the layout of the stalls directly depends on the number of cows and the milking machine used.
Walking area arrangement
Even a small barn for 10 heads should have a convenient walking area. Adult cows are sent out for grazing in the warm season, but young animals and bulls walk in the paddock during the day, and sometimes at night.
A barn for 20 heads can have several paddocks. It is important to maintain a distance of at least two meters between the walls of the pens to protect animals from injury (if you plan to simultaneously walk bulls - sires or young bulls).
